
Tuples are immutable and cannot be deleted.Dictionary can return the list of tuples by calling items, where each tuple is a key value pair.We must use tuple as the key if we need to create a composite key to use in a dictionary.A comparison operator in Python can work with tuples.In packing, we place value into a new tuple while in unpacking we extract those values back into variables.Python has tuple assignment feature which enables you to assign more than one variable at a time. If you have data that is immutable, implementing it as tuple will guarantee that it remains write-protected.Tuples that consist of immutable elements can be used as key for dictionary, which is not possible with list.Iterating through tuple is faster than with list, since tuples are immutable.To perform different task, tuple allows you to use many built-in functions like all(), any(), enumerate(), max(), min(), sorted(), len(), tuple(), etc.
Python tuple unpacking code#
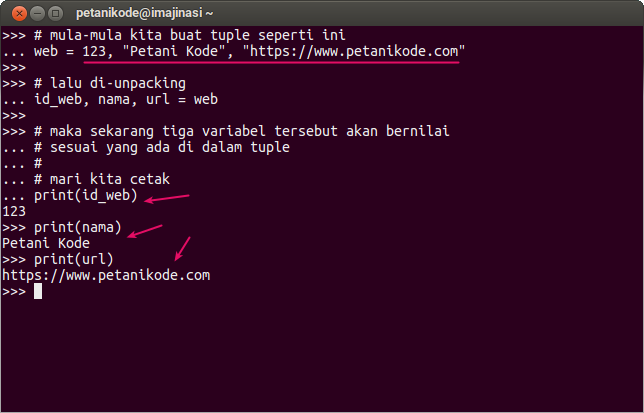
Here is the Python 2 Code for all above example tup1 = ('Robert', 'Carlos','1965','Terminator 1995', 'Actor','Florida') The output of this code will be (‘c’, ‘e’). Slicing is not only applicable to tuple but also for array and list. To fetch specific sets of sub-elements from tuple or list, we use this unique function called slicing. Tuple packing and unpacking solves the problem. But deleting tuple entirely is possible by using the keyword del Slicing of Tuple You cannot delete or remove items from a tuple. In Python, unpacking is not limited to tuples only. Tuples are immutable and cannot be deleted. Python tuple unpacking means pulling values apart from a tuple. It assigns the elements of each tuple to last and first and then prints the name and corresponding telephone number.ĭictionary can return the list of tuples by calling items, where each tuple is a key value pair. In unpacking of tuple number of variables on LHS should be equal to number of values in given tuple. In other way it is called unpacking of a tuple of values into a variable. it assigns (RHS)right hand side of values into (LHS)Left hand side.


Tuples are sequences, the tuples cannot be changed and tuples use parentheses. This loop navigates the keys in the directory, which are tuples. Tuple: In Python tuples are used to store immutable object.A tuple is a sequence of immutable Python objects. for last, first in directory: print first, last, directory is used to specify the arbitrary number of arguments in the tuple.
Python tuple unpacking how to#
The following code explains how to deal with an arbitrary number of arguments. We could use tuple assignment in a for loop to navigate this dictionary. In python tuples can be unpacked using a function in function tuple is passed and in function, values are unpacked into a normal variable. Inside the brackets, the expression is a tuple. This operation is known as tuple packing: record 2, 'John', 'Doe', 'Sales' print(record) Wise versa, you can extract tuple values back into variables. A tuple can be created without using parentheses. Assuming that we have declared the variables as last and first number, we could write a dictionary assignment statement as shown below: directory = number defining tuple of one element a 1, alternative way a tuple(1) Packing and unpacking Python tuples. Since tuples are hashable, and list is not, we must use tuple as the key if we need to create a composite key to use in a dictionary.Įxample: We would come across a composite key if we need to create a telephone directory that maps, first-name, last-name, pairs of telephone numbers, etc. So it goes into the else block and prints “b is bigger.” Using tuples as keys in dictionaries 6>4, so the output a is biggerĬase 3: Comparison starts with a first element of each tuple. In this case 5>1, so the output a is biggerĬase 2: Comparison starts with a first element of each tuple. It starts with comparing the first element from each of the tuplesĬase1: Comparison starts with a first element of each tuple. If they do not compare to =, then it proceed to the second element and so on. The comparison starts with a first element of each tuple. (company, emp, profile) = x # tuple unpackingĪ comparison operator in Python can work with tuples. Python Dictionaries Access Items Change Items Add Items Remove Items Loop Dictionaries Copy Dictionaries Nested Dictionaries Dictionary Methods Dictionary Exercise Python If.Else Python While Loops Python For Loops Python Functions Python Lambda Python Arrays Python Classes/Objects Python Inheritance Python Iterators Python Scope Python Modules Python Dates Python Math Python JSON Python RegEx Python PIP Python Try.X = ("Guru99", 20, "Education") # tuple packing


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
